Introduction: In the realm of glass manufacturing, precision cutting and shaping are critical processes that determine the quality and functionality of glass products. Traditional methods of cutting and shaping glass often lacked accuracy and consistency, leading to variations in product quality. However, with the advent of Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machinery, the glass manufacturing industry has witnessed a revolution in its production processes. This article delves into the significance of CNC machinery in precision cutting and shaping of glass and its impact on the industry.
The Evolution of Glass Cutting and Shaping: Historically, glass cutting and shaping were performed manually using rudimentary tools such as diamond-tipped blades and hand-operated cutters. While these methods served their purpose, they were limited in terms of precision and efficiency. Moreover, shaping intricate designs and complex curves was challenging and often resulted in wastage of material.
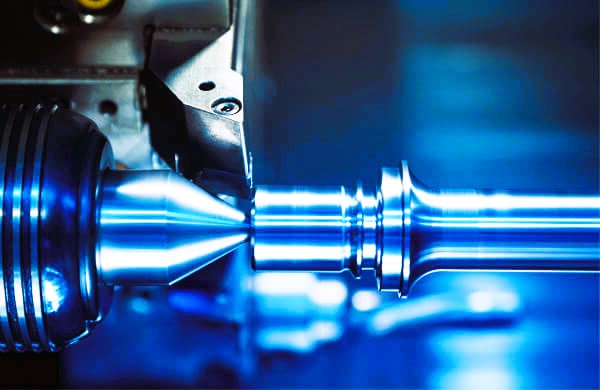
The Introduction of CNC Machinery: The introduction of Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machinery marked a paradigm shift in glass manufacturing. CNC machines utilize advanced computer technology to precisely control the movement of cutting and shaping tools. This level of automation enables manufacturers to achieve unprecedented levels of accuracy and repeatability in their production processes.
Precision Cutting with CNC Machinery: One of the primary functions of CNC machinery in glass manufacturing is precision cutting. CNC cutting machines are equipped with high-speed rotating blades or diamond-tipped tools that can accurately cut glass sheets to precise dimensions. Whether it’s straight cuts, curves, or intricate patterns, CNC machines can execute complex cutting tasks with unparalleled precision.
The Role of CAD Software: Central to the operation of CNC machinery is Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software. Design engineers create digital blueprints of glass products, specifying dimensions, shapes, and cutting patterns. These designs are then translated into machine-readable instructions by the CAD software, guiding the CNC machines during the cutting process. This seamless integration of design and manufacturing ensures accuracy and consistency in the final products.
Shaping and Profiling: In addition to cutting, CNC machinery is also used for shaping and profiling glass components. Whether it’s beveling, grinding, or polishing, CNC machines can accurately shape glass edges and surfaces to meet precise specifications. This capability is particularly valuable in architectural glass applications, where custom shapes and finishes are often required to meet design requirements.
Quality Assurance and Consistency: One of the key advantages of CNC machinery is its ability to deliver consistent results with minimal variability. Unlike manual methods, which are susceptible to human error and inconsistency, CNC machines adhere strictly to programmed instructions, ensuring uniformity across production batches. This level of precision and repeatability is essential for meeting quality standards and customer expectations. Read more about quality control in glass production in our article.
Safety Considerations: While CNC machinery offers numerous benefits in terms of precision and efficiency, it also poses certain safety considerations. Glass manufacturing facilities must adhere to strict safety protocols to ensure the safe operation of CNC machines. This includes proper training for machine operators, regular maintenance of equipment, and implementation of safety guards and emergency stop mechanisms.
Conclusion: In conclusion, CNC machinery plays a pivotal role in glass manufacturing, particularly in precision cutting and shaping processes. By harnessing the power of automation and computer-controlled technology, manufacturers can achieve higher levels of accuracy, consistency, and efficiency in producing glass products. As the industry continues to evolve, CNC machinery will remain a cornerstone of modern glass manufacturing, driving innovation and shaping the future of the industry.
For more information on glass manufacturing standards and regulations, please visit Wikipedia.

